CfIR Proposes a New Occupant Protection Rating System: The U.S., European and Australian NCAP and the IIHS produce ratings of new vehicle performance based on dynamic crash tests in frontal, side and rear crashes, and vehicle handling tests. No dynamic-based crashworthiness ratings exist to date for new vehicle performance based on rollover crashes. There is no rating for rollover occupant protection, a crash mode responsible for one-third of all light vehicle occupant fatalities. NHTSA has upgraded the roof crush requirements for new cars, but the time is overdue for an NCAP rating on rollover survivability. We have conducted extensive testing that provides a basis for such a rating. In particular the JRS dynamic rollover test results, in conjunction with NHTSA and IIHS statistical analyses, and the biomechanical injury correlation studies¹ provide that basis. A consumer rollover rating system is long overdue. The best way to rate the crashworthiness injury potential of vehicles in rollovers is by utilizing a JRS dynamic test. Rating vehicles simply by FMVSS 216 gives grossly misleading (both over and understated) injury rate results.²
FMVSS 216/216A: Safercar.gov publishes vehicle safety information serving the public interest. The site provides “star ratings” of U.S. vehicles in all accident modes. The rollover ratings are based on an SSF.
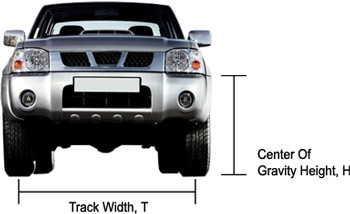
The SSF of a vehicle is an at-rest calculation of its rollover resistance based on its most important geometric properties. The SSF is a measure of how top-heavy vehicle is. The SSF only tells you how likely it is for the vehicle to rollover, NOT how well the vehicle structure will hold up if it does roll!
A vehicle's SSF is calculated using the formula SSF = T/2H, where T is the “Track Width“ and H is the “Height of the CG.” The track width is the distance between the centers of the right and left tires along the axle. The location of the CG is measured in a laboratory represents the height above the ground of the vehicle's mass. The lower the SSF number, the more likely the vehicle is to roll over in a single-vehicle crash.
FMVSS 216 Ratings: When evaluating a rating system based solely on FMVSS 216, in comparison to dynamic testing, anomalies abound. The Honda CRV is one such anomaly. The Honda CRV emulates the rollover roof crush performance of vehicles like the Volvo XC-90 and the VW Jetta with a high SWR. The Honda CRV may be a geometry-derived implementation of a roof improvement.
JRS Ratings: JRS dynamic tests were performed on 10 vehicles. Three of the vehicles tested earned “good” ratings, two were “acceptable”, two were “marginal” and three were rated “poor”.
Proposed CfIR Rating System: The proposed system includes a factored and weighted analysis by fatality rate and vehicle performance frequency in all major accident modes.
References:
